D&C
About D&C
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a procedure to remove tissue from inside your uterus. Health care professionals perform dilation and curettage to diagnose and treat certain uterine conditions — such as heavy bleeding — or to clear the uterine lining after a miscarriage or abortion.
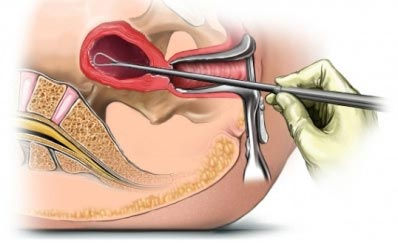
In a dilation and curettage, small instruments or a medication is used to open (dilate) the lower, narrow part of your uterus (cervix). Next, a surgical instrument called a curette, which can be a sharp instrument or suction device, is used to remove uterine tissue.
To diagnose a condition
Before doing a D&C, your health care team might recommend a procedure called endometrial biopsy or endometrial sampling to diagnose a condition. Endometrial sampling might be done if:
-
You have unusual uterine bleeding.
-
You have bleeding after menopause.
-
You have unusual endometrial cells, which are discovered during a routine test for cervical cancer.
To perform the test, a health care professional collects a tissue sample from the lining of your uterus, also called the endometrium, and sends the sample to a lab for testing.
To treat a condition
When performing a D&C to treat a condition, a doctor removes the contents from inside your uterus, not just a small tissue sample. This might be done to:
-
Prevent infection or heavy bleeding by clearing tissues that remain in the uterus after a miscarriage or abortion.
-
Remove a tumour that forms instead of a typical pregnancy. This is also called a molar pregnancy.
-
Treat excessive bleeding after delivery by clearing out any placenta that remains in the uterus.
-
Remove cervical or uterine polyps, which are usually noncancerous, or benign.
A D&C might be combined with another procedure called hysteroscopy. During hysteroscopy, a doctor inserts a slim instrument with a light and camera on the end into your vagina, through your cervix and into your uterus.
At times, a hysteroscopy might be done combined with an endometrial biopsy before a full D&C procedure.